jeudi 30 novembre 2023
SCIENCES ENERGIES ENVIRONNEMENT
mercredi 29 novembre 2023
SCIENCES ENERGIES ENVIRONNEMENT
Physicists find evidence of exotic charge transport in quantum material
mardi 28 novembre 2023
SCIENCES ENERGIES ENVIRONNEMENY
Telescope Array detects second-highest-energy cosmic ray ever
lundi 27 novembre 2023
SCOENCES ENERGIES ENVIRONNEMENT
Here is your customized Science X Newsletter for week 47:
 | Telescope Array detects second-highest-energy cosmic ray everIn 1991, the University of Utah Fly's Eye experiment detected the highest-energy cosmic ray ever observed. Later dubbed the Oh-My-God particle, the cosmic ray's energy shocked astrophysicists. Nothing in our galaxy had the power to produce it, and the particle had more energy than was theoretically possible for cosmic rays traveling to Earth from other galaxies. Simply put, the particle should not exist. |
 | Study examines how massive 2022 eruption changed stratosphere chemistry and dynamicsWhen the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai volcano erupted on January 15, 2022 in the South Pacific, it produced a shock wave felt around the world and triggered tsunamis in Tonga, Fiji, New Zealand, Japan, Chile, Peru and the United States. |
 | Physicists find evidence of exotic charge transport in quantum materialTrue to form, a "strange metal" quantum material proved strangely quiet in recent quantum noise experiments at Rice University. Published this week in Science, the measurements of quantum charge fluctuations known as "shot noise" provide the first direct evidence that electricity seems to flow through strange metals in an unusual liquidlike form that cannot be readily explained in terms of quantized packets of charge known as quasiparticles. |
 | New constraints on the presence of ultralight dark matter in the Milky WayDark matter, composed of particles that do not reflect, emit or absorb light, is predicted to make up most of the matter in the universe. Its lack of interactions with light, however, prevents its direct detection using conventional experimental methods. |
 | Archaeologists uncover Europe's hidden Bronze Age megastructuresArchaeologists from University College Dublin, working with colleagues from Serbia and Slovenia, have uncovered a previously unknown network of massive sites in the heart of Europe that could explain the emergence of the continent's Bronze Age megaforts—the largest prehistoric constructions seen prior to the Iron Age. |
 | Physiological and archaeological evidence rewrites assumptions about a gendered division of labor in prehistoric timesPrehistoric men hunted; prehistoric women gathered. At least this is the standard narrative written by and about men to the exclusion of women. |
 | Global view of Io's volcanic activity suggests that tidal heating is concentrated within its upper mantleA team of volcanologists and planetary scientists from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, the University of Arizona, and Arizona State University has found via study of a newly created global view of Io's volcanic activity that its tidal heating is likely concentrated within its upper mantle. In their study, reported in the journal Nature Astronomy, the group analyzed data from sensors measuring heat emission from the closest of Jupiter's innermost moons. |
 | Research challenges widespread belief that honeybees naturally insulate their colonies against coldA Leeds researcher is keen to help beekeepers shape their practices following his study which appears to disprove the widespread belief that honeybees naturally insulate their colonies against the cold. His findings suggest that the creatures are potentially being subjected to thermally-induced stress. |
 | The bilingual brain may be better at ignoring irrelevant informationPeople who speak two languages may be better at shifting their attention from one thing to another compared to those who speak one, according to a study published this month in the journal Bilingualism: Language and Cognition. |
 | World's richest 1% emit as much carbon as bottom two-thirds: reportThe richest one percent of the global population are responsible for the same amount of carbon emissions as the world's poorest two-thirds, or five billion people, according to an analysis published Sunday by the nonprofit Oxfam International. |
 | Residential solar power saves less energy than expectedImagine a household that consumes 1,000 kilowatt hours of energy per month. Then they install solar panels on their roof that generate 500 kilowatt hours of electricity per month on average. How much should their consumption of electricity drawn from the power grid decline after they install solar? Five hundred kilowatt hours is the expectation, but in reality, it's less than that for most people. Now, they're consuming more than 1,000 kilowatt hours per month. |
 | AI finds formula for how to predict monster waves by using 700 years' worth of dataLong considered myth, freakishly large rogue waves are very real and can split apart ships and even damage oil rigs. Using 700 years' worth of wave data from more than a billion waves, scientists at the University of Copenhagen and University of Victoria have used artificial intelligence to find a formula for how to predict the occurrence of these maritime monsters. The new knowledge can make shipping safer. |
 | Bacteria store 'memories' and pass them on for generations, study findsScientists have discovered that bacteria can create something like memories about when to form strategies that can cause dangerous infections in people, such as resistance to antibiotics and bacterial swarms when millions of bacteria come together on a single surface. The discovery—which has potential applications for preventing and combatting bacterial infections and addressing antibiotic-resistant bacteria—relates to a common chemical element bacterial cells can use to form and pass along these memories to their progeny over later generations. |
 | 'Triple star' discovery could revolutionize understanding of stellar evolutionA ground-breaking new discovery by University of Leeds scientists could transform the way astronomers understand some of the biggest and most common stars in the universe. The paper, "Gaia uncovers difference in B and Be star binarity at small scales: evidence for mass transfer causing the Be phenomenon," is published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. |
 | Research reveals rare metal could offer revolutionary switch for future quantum devicesQuantum scientists have discovered a rare phenomenon that could hold the key to creating a 'perfect switch' in quantum devices which flips between being an insulator and a superconductor. |
 | AI system self-organizes to develop features of brains of complex organismsCambridge scientists have shown that placing physical constraints on an artificially-intelligent system—in much the same way that the human brain has to develop and operate within physical and biological constraints—allows it to develop features of the brains of complex organisms in order to solve tasks. |
 | New carbon material sets energy-storage record, likely to advance supercapacitorsGuided by machine learning, chemists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory designed a record-setting carbonaceous supercapacitor material that stores four times more energy than the best commercial material. A supercapacitor made with the new material could store more energy—improving regenerative brakes, power electronics and auxiliary power supplies. |
 | Fossil unearthed in Mongolia's Gobi Desert suggests some dinosaurs slept in same position as modern birdsA team of paleontologists and biologists from Hokkaido University, Hokkaido University Museum, North Carolina State University and the Mongolian Academy of Sciences, has uncovered a previously unknown species of dinosaur that appears to have slept in the same position as modern birds. |
 | Scientists finally succeed in growing dolomite in the lab by dissolving structural defects during growthFor 200 years, scientists have failed to grow a common mineral in the laboratory under the conditions believed to have formed it naturally. Now, a team of researchers from the University of Michigan and Hokkaido University in Sapporo, Japan have finally succeeded, thanks to a new theory developed from atomic simulations. |
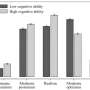 | Higher levels of financial optimism associated with lower levels of cognitive abilityA behavioral economist at the University of Bath in the U.K. has found evidence linking higher levels of unwarranted financial optimism with lower levels of cognitive ability. In his study, published in the journal Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, Chris Dawson surveyed thousands of people in the U.K. about their economic outlook and compared their responses with their true financial outlook. XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX |
dimanche 26 novembre 2023
SCIENCES ENERGIES ENVIRONNEMENT
L article dont je commence la discussion aujourd hui a fait l'objer d 'une traduction puis d une présentation sur le site SCIRENCES ENERRGIES ENVIRONNEMENT /BLOGGER il ya quelques semaines ;.
"Phys.org
https://phys.org › Physics › General Physics
Oct 18, 2023 — Charles H. Lineweaver et al, All objects and some questions, American Journal of Physics (2023). DOI: 10.1119/5.0150209.
L article dont je commence la discussion aujourd hui a fait l'objer d 'une traduction puis d une présentation sur le site SCIRENCES ENERRGIES ENVIRONNEMENT /BLOGGER il ya quelques semaines ;.
"Phys.org
https://phys.org › Physics › General Physics
Oct 18, 2023 — Charles H. Lineweaver et al, All objects and some questions, American Journal of Physics (2023). DOI: 10.1119/5.0150209.
''lLa vision la plis complète de l’univers jamais créée a été produite par des chercheurs de l’Université nationale australienne (ANU). L’étude propose également de nouvelles idées sur la façon dont notre univers a pu commencer.''
Le graphique ci dessus vous présente encoordonnée log og la densiye des divers types de masses d objerts de notre univers et la temerature .
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
L"article de SCIENCE X formule lui
explicitement la meme hypothèse que celle der mon ami Frederic Cardoso ;l' histoire thermique de l univers se situe dans un cadre ou le parametre temps n est pas représenté :l 'univers démarre d un trou noir géant mais quand comment pourquoi ?...Ca ni SCIENCE X ni mon ami ne me le dise,t !!
La partie la plus interessante de leur graphique est cette droite qui est tracée entre l 'objet le plus petit et le plus froid possible qui est un corps noir de Scwarzchild minimal minimorum et le point extrme resultant du poimt de rencotre entre le ryon de HUBBLE et la relativite generale ...C 'est le point de départ supposé du BIGBANG
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Selon les auteurs tous les types de trous noirs possibles se trouvent sur cette diagogonale et celle ci crée une zone mysterieuse et inexpliquée par les équations actuelles de la gravité .
Un des points importants de l 'article est la positoon que prend l auteur pour situer une sur autre doite la décroissance de l température au fur et a mesure que l univers vieillit et que sa dendité globale diminue .....
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Plusieurs questions sont posées par les auteurs originaux dans la conclusion de leur communication que je vous ai présenté le dimanche 19 novembre et je me les pose autrement ;
1 / Les aires interdites pai la gravité et par la limite de COMPTON correspondent elles a une connaisance incoplète de la physique utilisée par l auteur ?
2 / Quel est le processus quui peut expliquer qu un trou noir géantissime
trés froid se propulse du point triangulaire noir en bas au point BIG BANG en haut ?
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pour essayer de progresser j ai lancé une recherche bibloigraphiquue :que nous disent nos messures sur les trous noirs ,?
On ignore leur temperature réelle mais leur extreme densité montre que leur contenu garde ENCORE les caractéristiques d une masse pour expliquer leur pouvoir d attraction par gravité ... Leur composition interne est elle homogène ( que des quarks ,des neutrons ,des neutrinos un condensat de BOSE EONSTEIN etc ) ? Aucune théorie ne s 'y frotte ,sauf des physiciens anarchistes
oyhérétiques !!!Je réponds donc a Fredéric ; POUR L INSTANT je e n'ai rien à te proposer pour transformer illico presto
un tou noir géant gelé en trou noir géant que sa température /densitéva faire exploser !!!! Inurle d invoquer les manes de STEPHENS et son rayonnement !
A suivre dimanche prochain !
''lLa vision la plis complète de l’univers jamais créée a été produite par des chercheurs de l’Université nationale australienne (ANU). L’étude propose également de nouvelles idées sur la façon dont notre univers a pu commencer.''
Le graphique ci dessus vous présente encoordonnée log og la densiye des divers types de masses d objerts de notre univers et la temerature .
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
L"article de SCIENCE X formule lui
explicitement la meme hypothèse que celle der mon ami Frederic Cardoso ;l' histoire thermique de l univers se situe dans un cadre ou le parametre temps n est pas représenté :l 'univers démarre d un trou noir géant mais quand comment pourquoi ?...Ca ni SCIENCE X ni mon ami ne me le dise,t !!
La partie la plus interessante de leur graphique est cette droite qui est tracée entre l 'objet le plus petit et le plus froid possible qui est un corps noir de Scwarzchild minimal minimorum et le point extrme resultant du poimt de rencotre entre le ryon de HUBBLE et la relativite generale ...C 'est le point de départ supposé du BIGBANG
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Selon les auteurs tous les types de trous noirs possibles se trouvent sur cette diagogonale et celle ci crée une zone mysterieuse et inexpliquée par les équations actuelles de la gravité .
Un des points importants de l 'article est la positoon que prend l auteur pour situer une sur autre doite la décroissance de l température au fur et a mesure que l univers vieillit et que sa dendité globale diminue .....
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Plusieurs questions sont posées par les auteurs originaux dans la conclusion de leur communication que je vous ai présenté le dimanche 19 novembre et je me les pose autrement ;
1 / Les aires interdites pai la gravité et par la limite de COMPTON correspondent elles a une connaisance incoplète de la physique utilisée par l auteur ?
2 / Quel est le processus quui peut expliquer qu un trou noir géantissime
trés froid se propulse du point triangulaire noir en bas au point BIG BANG en haut ?
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pour essayer de progresser j ai lancé une recherche bibloigraphiquue :que nous disent nos messures sur les trous noirs ,?
On ignore leur temperature réelle mais leur extreme densité montre que leur contenu garde ENCORE les caractéristiques d une masse pour expliquer leur pouvoir d attraction par gravité ... Leur composition interne est elle homogène ( que des quarks ,des neutrons ,des neutrinos un condensat de BOSE EONSTEIN etc ) ? Aucune théorie ne s 'y frotte ,sauf des physiciens anarchistes
oyhérétiques !!!Je réponds donc a Fredéric ; POUR L INSTANT je e n'ai rien à te proposer pour transformer illico presto
un tou noir géant gelé en trou noir géant que sa température /densitéva faire exploser !!!! Inurle d invoquer les manes de STEPHENS et son rayonnement !
A suivre dimanche prochain !
samedi 25 novembre 2023
SCIENCES ENERGIES ENVIRONNEMENT






